MAPF Planner Integration#
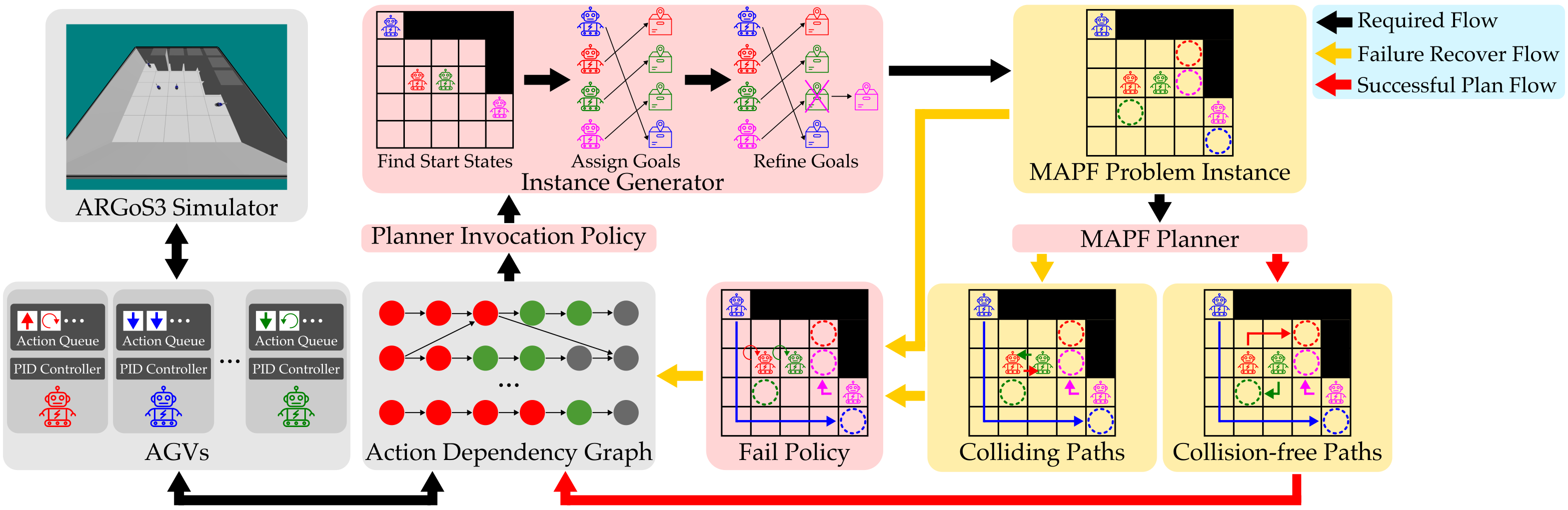
The MAPF planner takes in a MAPF problem instance with a time limit and returns collision-free paths within that time limit. The MAPF planner should return colliding paths in case of failure if the fail policy expects them.
Our Provided Planners#
We provide several built-in MAPF planners, including:
RHCR (Li et al. 2021): the Rolling Horizon Collision Resolution planner. RHCR plans for windowed paths for all robots. It supports planning with the pebble motion model and rotational motion model. RHCR is the default planner in LSMART.
MASS (Yan et al. 2025): the MAPF-SSIPP-SPS planner. MASS plans for full-horizon paths with 2nd order dynamics for all robots.
PBS (Ma et al. 2019): the Priority-Based Search planner . PBS plans for full-horizon paths for all robots. It supports planning with the pebble motion model.
TPBS (Morag et al. 2025): the Transient Priority-Based Search planner . TPBS plans for full-horizon paths for all robots even if there are duplicate goals. It supports planning with the pebble motion model.
Detailed usage of the built-in planners can be found in the Quick Start with Python API guide.
Add New Planners#
The MAPF planners use RPC to communicate with other modules in LSMART. Specifically, the planner shall implement an RPC client that connects to the RPC server in LSMART. The planner shall receive a MAPF problem instance and a time limit from LSMART, and return collision-free paths within that time limit.
Check LSMART Initialization and Invocation Status#
Since RPC is a one-way communication protocol, the MAPF planner shall first check with the RPC server in LSMART whether the system is initialized and whether the planner should be invoked before attempting to receive a MAPF problem instance.
To check if other modules of LSMART are initialized, the MAPF planner shall use a RPC client to invoke the following function:
-
bool rpc_api::isInitialized()#
Check if the system has been initialized.
- Returns:
a boolean indicating whether the system has been initialized.
To check if the planner should be invoked, the MAPF planner shall use a RPC client to invoke the following function:
Receive MAPF Problem Instances#
The MAPF planner shall use a RPC client to invoke the getRobotsLocation to receive a MAPF problem instance from LSMART.
-
string rpc_api::getRobotsLocation()#
Get the latest MAPF instance, newly finished task IDs, and initialization status.
- Returns:
A JSON string with the following schema.
{ "initialized": true, "mapf_instance": { "starts": [ State, ... ], "goals": [ [ Task, ... ], ... ] }, "new_finished_tasks": [ 0, 1, 2, 3 ] }initializedindicates whether the system has completed initialization.mapf_instancecontains the current MAPF problem state:startsis a list ofStateobjects describing the current start states of all agents:Each
Statehas the structure:{ "location": 42, "timestep": 10, "orientation": 1 }
locationis the flattened cell ID.timestepis the start timestep, usually0.orientationis encoded as:0: East1: North2: West3: South
goalsis a list of task lists, where each task list corresponds to a robot:Each
Taskobject has the structure:{ "id": 0, "location": 84, "task_wait_time": 0, "orientation": -1 }
idis the unique task identifier.locationis the flattened cell ID of the task location.task_wait_timeis the number of timesteps the agent should wait at the task location, usually0.orientationis the required orientation at the task location, with-1indicating no constraint.
new_finished_tasksis a list of task IDs completed since the last query.
Return Plan Results#
After planning, no matter success or failure, the MAPF planner shall use a RPC client to invoke the following function to return the plan results to LSMART:
-
void rpc_api::addNewPlan(string &new_plan_json_str)#
Add a new MAPF plan to the ADG.
This function takes a JSON string representing a new MAPF plan and adds it to the ADG (Action Decision Graph). If necessary, it utilizes the backup planner to ensure the plan is integrated correctly.
- Parameters:
new_plan_json_str – A JSON string with a new MAPF plan with the following schema:
{ "success": true, "plan": [ [(row, col, timestep, task_id), ... ], ... ], "congested": false, "stats": { ... } }plan: a list of lists of tuples, where each outer list corresponds to a single robot’s path. Each inner list contains tuples of the form(row, col, timestep, task_id):row: The row index of the robot’s position on the grid.col: The column index of the robot’s position on the grid.timestep: The timestep at which the robot should be at the specified position.task_id: The task identifier, or-1if no task is associated.
success: indicates whether the planner successfully produced collision-free paths for all robots. Iffalse, the backup planner is invoked.congested[Optional]: indicates whether congestion was detected, typically defined as more than half of the robots making no progress.stats[Optional]: contains additional planner statistics recorded by LSMART.